Tooth cyst is an odontogenic cyst, more common near the root canal. It usually has a liquid content. Cysts are the body's unique response to infection. One of the drawbacks of a cyst is its constant growth, which means that the healthy bone around the cyst is effected continuously. It is very dangerous for the teeth around it, as well as for the jaw.
Causes
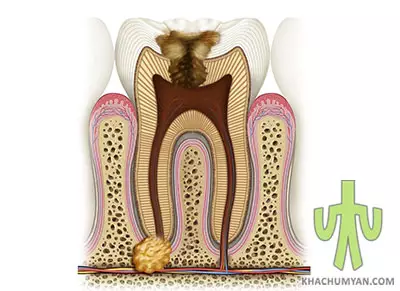 The main causes of cysts are infections and injuries. The infection penetrates mainly through the root canal. Sometimes it emerges as a recurrence of sinusitis, from where the infection penetrates the focus through the blood. The cyst may not have clinical signs for a very long time. Clinical signs appear when the cyst reaches a large size - 3-4 cm or when the body's resistance decreases, for example, during infectious diseases. And the area where the cyst is located is swollen and deformed. Worsening of dental cysts leads to purulent processes, which often end in tooth extraction. To avoid complications and removal, you should consult a dentist at the right time.
The main causes of cysts are infections and injuries. The infection penetrates mainly through the root canal. Sometimes it emerges as a recurrence of sinusitis, from where the infection penetrates the focus through the blood. The cyst may not have clinical signs for a very long time. Clinical signs appear when the cyst reaches a large size - 3-4 cm or when the body's resistance decreases, for example, during infectious diseases. And the area where the cyst is located is swollen and deformed. Worsening of dental cysts leads to purulent processes, which often end in tooth extraction. To avoid complications and removal, you should consult a dentist at the right time.
Treatment of a dental cyst
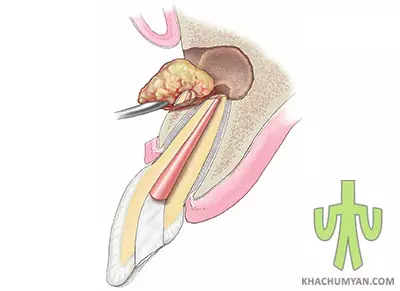 The earlier a cyst is discovered, the more it is likely that the tooth will be kept. The treatment of dental cyst can be carried out in two ways depending on the type and size of the cyst. The treatment can be conservative and surgical. In the case of the conservative type, the cavity is treated with special healing materials. Note that this method is only applicable to small cavities up to 8 mm.
The earlier a cyst is discovered, the more it is likely that the tooth will be kept. The treatment of dental cyst can be carried out in two ways depending on the type and size of the cyst. The treatment can be conservative and surgical. In the case of the conservative type, the cavity is treated with special healing materials. Note that this method is only applicable to small cavities up to 8 mm.
The surgical method is often used frequently. With this method, the cyst is removed; sometimes there can be a need of removing the adjacent tooth.
After the cyst removal, the dentist prescribes treatment, which includes rinsing with antiseptic, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory painkillers, as well as antibiotics.
Treatment of the cyst is more thriving in the beginning. Therefore, frequent visits to the dentist will allow examination of the previously treated root canals, which will help to avoid complications.



