Stomatitis is a common concept that includes inflammatory diseases of the oral mucous membrane. Stomatitis usually occurs as a result of the immune system's suppression. There are several types of stomatitis:
- Chronic recurrent aphthous (ulcerative) stomatitis
- Herpetic stomatitis
- Ulcerative stomatitis (Vincent's stomatitis)
- Candidiasis stomatitis
Chronic recurrent aphthous (ulcerative) stomatitis
 Chronic recurrent aphthous (ulcerative) stomatitis is manifested by specific aphthae (ulcers). It occurs on the lips, buccal mucosa (inner cheek area), palate, and tongue. Viruses and bacteria are considered causative agents. The disease clinically appears because of B1 and B12 vitamin imbalance. It is often associated with diseases related to the liver or gastrointestinal tract.
Chronic recurrent aphthous (ulcerative) stomatitis is manifested by specific aphthae (ulcers). It occurs on the lips, buccal mucosa (inner cheek area), palate, and tongue. Viruses and bacteria are considered causative agents. The disease clinically appears because of B1 and B12 vitamin imbalance. It is often associated with diseases related to the liver or gastrointestinal tract.
Herpetic stomatitis
 The main cause of herpetic stomatitis is herpes simplex virus, less common is herpes zoster. It is often found in children aged 1-3 years. Moreover, children initially experience general intoxication signs such as
The main cause of herpetic stomatitis is herpes simplex virus, less common is herpes zoster. It is often found in children aged 1-3 years. Moreover, children initially experience general intoxication signs such as
- Total body weakness
- High fever
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
Afterward, blisters are formed on the oral mucosa, as well as on vermillion borders of the lips, which open very quickly and cause erosions with rough edges.
Ulcerative stomatitis (Vincent's stomatitis)
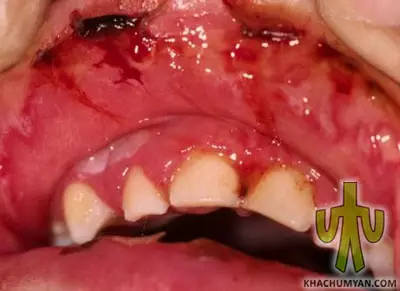 Vincent's ulcerative stomatitis is characterized by necrosis of the gingival margin. Often, the disease firstly infects the gingival sulcus and the gum i.e. the adjacent mucous membranes. Because of this disease painful, bleeding ulcers appear which quickly join together forming large defects in the mucous membrane. Usually an unpleasant odor comes from the mouth which is evidence of the active process of necrosis. Surely it can be also the result of poor hygiene. This type of stomatitis is more common in the 17-30 age groups. Vincent's ulcerative stomatitis can be accompanied by influenza, angina, various blood diseases, AIDS, tuberculosis, and cause unpleasant and severe complications.
Vincent's ulcerative stomatitis is characterized by necrosis of the gingival margin. Often, the disease firstly infects the gingival sulcus and the gum i.e. the adjacent mucous membranes. Because of this disease painful, bleeding ulcers appear which quickly join together forming large defects in the mucous membrane. Usually an unpleasant odor comes from the mouth which is evidence of the active process of necrosis. Surely it can be also the result of poor hygiene. This type of stomatitis is more common in the 17-30 age groups. Vincent's ulcerative stomatitis can be accompanied by influenza, angina, various blood diseases, AIDS, tuberculosis, and cause unpleasant and severe complications.
Except for blisters, there can be other symptoms including intoxication, fever as well as swelling of the lymph nodes.
Candidiasis stomatitis
 This type of stomatitis is very common. The causative agents are the fungus of Candida.
This type of stomatitis is very common. The causative agents are the fungus of Candida.
The main symptoms are
- Dry mouth
- Oral dysaesthesia – a burning feeling
- Creamy, white curd-like patches in the mouth (in the case of removal, the mucous membrane starts bleeding).
Treatment of stomatitis
At the first signs, you should see a dentist. It cannot be treated on its own, as relevant medications are prescribed depending on the type of disease and the clinic. The first important step is the accurate diagnosis, the second is the elimination of the disease causes and the third is the symptomatic therapy, which is the complete and final stage of treatment.
Prevention
To prevent disease, you should take care of mouth hygiene properly and regularly. While at the first signs, you should see a specialist avoid further disease complications.

